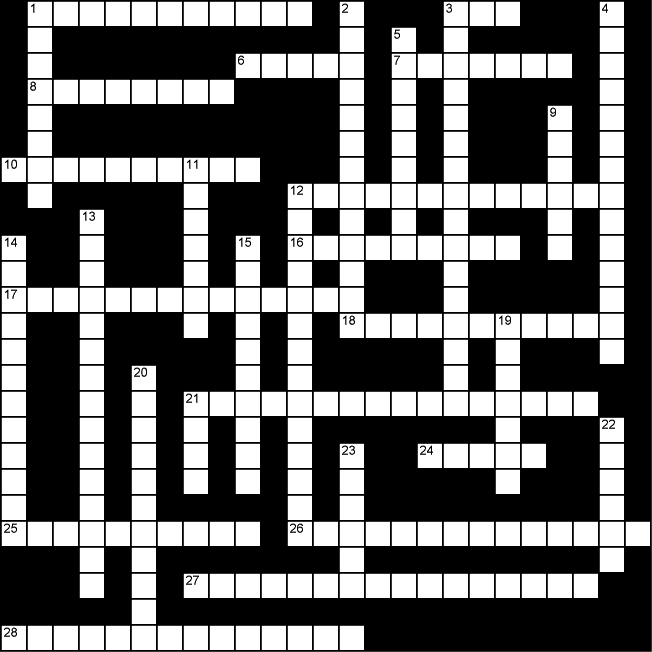
| 1 | | Adjustments in exchange rate
conversions that take into account
differences in the true cost of
living across nations is called
purchasing ______. (5,6) |
| 3 | | This measures total income
accruing to Canadian residents in
the current year. (3) |
| 6 | | Total spending on new capital
goods in the current year, not
including changes in inventories,
is called ______investment. (5) |
| 7 | | Total dollar amount spent by
Canadians on goods produced in
foreign nations. (7) |
| 8 | | Items that are consumed and
produced at the same time. (8) |
| 10 | | The dollar value of an industry's sales minus the value of intermediate goods is called ______. (5,5) |
| 12 | | ______ measures the net addition
to the nation's capital stock in the current year. (3,10) |
| 16 | | Dollars spent on programs such as
welfare and employment benefits
are called government ______. (9) |
| 17 | | The amount of income that
households actually receive before
they pay personal taxes. (8,6) |
| 18 | | Economic development that meets
the needs of the present without
compromising the ability of future
generations is called ______
development. (11) |
| 21 | | Corporate ______refer to profit
earned during the current year
that is not taxed or paid out to
shareholders. (8,8) |
| 24 | | Goods that are at their final
stage of production and will not be
further processed are called
______ goods. (5) |
| 25 | | Total value of exports minus
imports in the current year equals
______. (3,7) |
| 26 | | Increases in per capita real GDP
measured by its rate of change per
year is called ______. (8,6) |
| 27 | | ______is another term for capital
goods. (8,8) |
| 28 | | The amount that is left over from
disposable income after deducting
consumption in the current year. (8,6) |